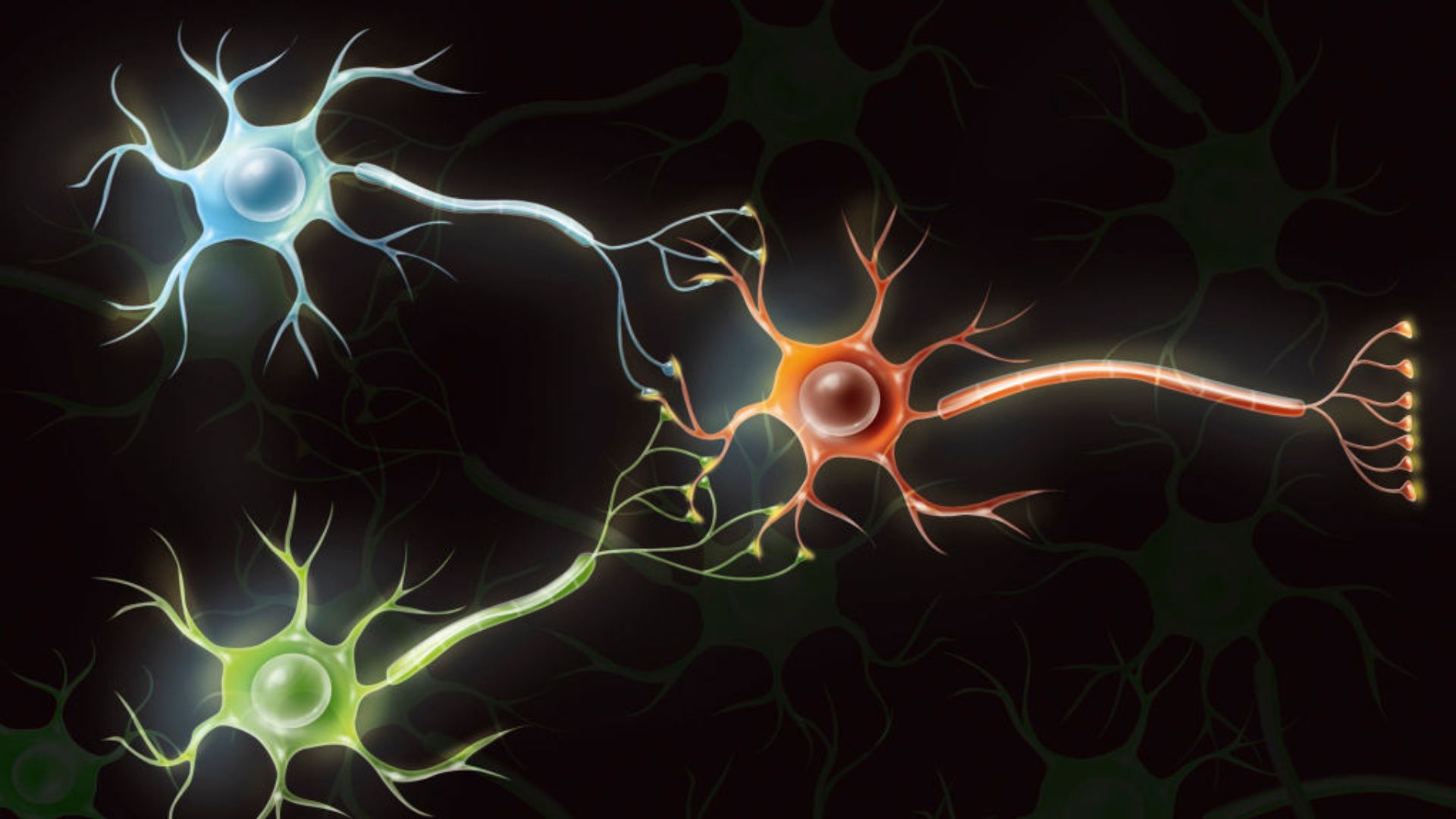
Researchers have successfully transformed human brain cells into functional computers, a groundbreaking achievement that could revolutionize computing. This innovative approach, known as a biocomputer, utilizes biologically derived materials such as DNA, proteins, and living tissue, specifically lab-grown neurons, to perform computational tasks.
The findings were published in the prestigious journal Nature and represent a significant step forward in the field of bioengineering. The team, led by scientists at the University of California, San Diego, emphasized that this technology could potentially lead to more efficient computing systems that mimic human brain functions.
Harnessing Biological Materials for Computation
Biocomputers differ from traditional electronic computers by leveraging the unique properties of biological materials. By integrating living cells into computational frameworks, researchers can achieve complex processing tasks that conventional silicon-based systems struggle with. The use of lab-grown neurons allows for a level of adaptability and sophistication that is unmatched in current technology.
In their experiments, the scientists programmed the neurons to respond to various stimuli, enabling them to perform calculations and data processing. This advancement not only showcases the potential of biocomputing but also raises questions about the ethical implications of using human cells in technology.
The project aims to explore how biological systems can enhance computational efficiency. The researchers believe that biocomputers could lead to significant breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. With the ability to process information in ways similar to the human brain, these systems may surpass traditional computing methods in specific applications.
Future Implications and Ethical Considerations
As this technology develops, the implications for diverse fields are vast. In medicine, biocomputers could assist in creating more personalized treatment plans by analyzing patient data in real-time. In environmental science, they may help in monitoring ecosystems and responding to changes more rapidly.
Yet, the use of human brain cells raises ethical questions that must be addressed. The scientists are committed to ensuring that their research adheres to strict ethical guidelines. As they move forward, they will engage with ethicists, policymakers, and the public to discuss the potential risks and benefits of biocomputing.
The research team is optimistic about future collaborations that could accelerate the application of biocomputers in various sectors. Their work not only opens new avenues for technological advancement but also invites a broader discussion on the intersection of biology and technology.
In conclusion, the development of biocomputers using human brain cells marks a pivotal moment in both computer science and bioengineering. As this field continues to evolve, it holds promise for a future where technology and biology work hand in hand to solve some of the world’s most pressing challenges.