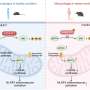
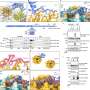
A team at UT Southwestern Medical Center has identified a molecular pathway that connects obesity to systemic inflammation. This discovery sheds light on the underlying mechanisms that increase the risk of several serious health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, and certain cancers.
The research, published in the journal *Nature*, marks a significant advancement in understanding how obesity contributes to chronic health issues. The findings indicate that a specific molecular “switch” activates inflammatory responses within the body, which can lead to these diseases. By clarifying this link, researchers hope to pave the way for new therapeutic targets that could mitigate the health impacts of obesity.
Understanding the role of this molecular pathway is crucial as obesity rates continue to rise globally. According to the World Health Organization, more than 1.9 billion adults were classified as overweight in 2021, with over 650 million of those considered obese. The implications of this research extend beyond individual health, affecting public health systems and economic stability worldwide.
Exploring the Mechanisms of Inflammation
The study highlights how the activation of this molecular switch initiates a cascade of inflammatory responses. Researchers utilized various laboratory models to demonstrate that the pathway could be targeted to reduce inflammation and its associated risks. The team believes that by inhibiting this pathway, it might be possible to decrease inflammation in individuals struggling with obesity.
Dr. J. Andrew H. Choi, the lead author of the study, emphasized the importance of these findings: “This research provides a clearer picture of how obesity can lead to chronic inflammation. Our aim is to develop targeted therapies that can intervene in this process and improve health outcomes for millions of people.”
The implications of this discovery are significant. If the molecular switch can be effectively targeted, it may lead to innovative treatments for conditions that are exacerbated by inflammation, ranging from metabolic disorders to various forms of cancer.
Potential for New Therapeutic Strategies
The research team is now focused on translating these findings into clinical applications. The next steps will involve testing potential drugs that can inhibit the inflammatory pathway in human trials. If successful, these therapies could provide a much-needed option for addressing the health challenges associated with obesity.
As healthcare professionals and researchers further explore this molecular pathway, there is hope for a future where obesity-related diseases can be managed more effectively. These efforts are critical, considering the global burden of obesity-related health issues, which not only affect individual health but also strain healthcare systems.
In summary, the identification of this molecular switch by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers represents a promising step toward understanding and treating the complex relationship between obesity and inflammation. The potential for new therapeutic options could lead to improved health outcomes for millions, marking a significant advancement in the fight against obesity-related diseases.