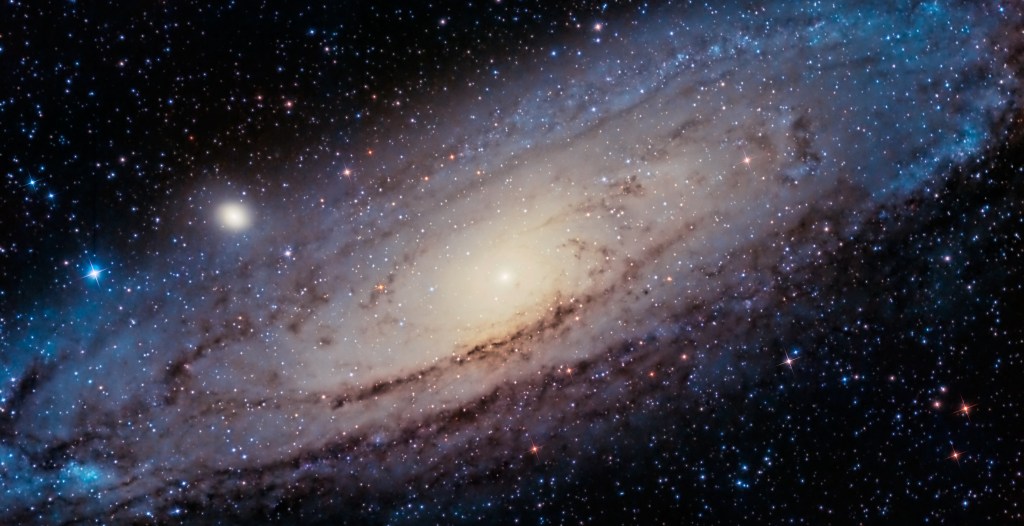
A recent study from Yonsei University led by astronomer Young-Wook Lee challenges the widely accepted notion that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. Published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, the research suggests that this acceleration may actually be an illusion, indicating that the universe has been slowing down for approximately 1.5 billion years.
The team’s findings are based on an analysis of Type Ia supernovae, which astronomers have traditionally used as cosmic measuring tools. These stellar explosions are thought to shine with consistent intrinsic brightness, allowing scientists to determine their distance from Earth based on their brightness. However, Lee’s team examined data from 300 galaxies and concluded that the brightness of these supernovae varies according to the age of the stars that produce them. Older stars tend to yield dimmer explosions, which could significantly alter the interpretation of cosmic distances.
In his statement, Lee emphasized the implications of their findings, saying, “Our study shows that the universe has already entered a phase of decelerated expansion at the present epoch and that dark energy evolves with time much more rapidly than previously thought.” This suggests that dark energy, a mysterious force driving the universe’s expansion, might not be constant but could change over time. If validated, this theory could redefine fundamental principles in cosmology, marking a significant shift since dark energy was first proposed in the late 1990s.
Despite the intriguing nature of this research, it has not gone without skepticism. Carlos Frenk, a cosmologist at the University of Durham, acknowledged the study’s provocative stance but remarked, “It’s definitely interesting. It’s very provocative. It may well be wrong.” This highlights the ongoing debates within the scientific community regarding the universe’s expansion.
The study exemplifies the dynamic nature of scientific inquiry, where new ideas can challenge long-held beliefs. As researchers continue to explore and debate these findings, the future of our understanding of the universe remains uncertain yet exciting. The pursuit of knowledge in astrophysics is an ever-evolving journey that captivates scientists and the public alike.
As the discourse around cosmic expansion unfolds, it underscores the importance of rigorous investigation and the willingness to question established theories. This research not only contributes to the understanding of the universe but also reflects the essence of scientific progress—constantly asking questions and seeking answers in the quest for knowledge.