Changes in taste perception are a common experience as individuals age, affecting how food is enjoyed and consumed. Researchers have identified that the sensitivity of taste buds diminishes over time, leading to both muted flavors and a reduced interest in food, which can have broader implications for health and nutrition.
According to a study conducted by the University of Kentucky, individuals over the age of 60 often experience a decreased ability to taste certain flavors, particularly sweet and salty. This decline can begin as early as the age of 50, with significant changes noted by the time individuals reach their 70s. The decline in taste sensitivity is attributed to a combination of biological changes and lifestyle factors.
Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Taste Decline
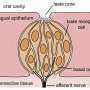
Taste buds, which are responsible for detecting flavors, can become less effective due to various reasons. As people age, the number of taste buds decreases, and the remaining buds may not function as efficiently. A study by the National Institute on Aging highlights that this reduction can lead to a diminished enjoyment of food, which is particularly concerning given the importance of nutrition in maintaining health in older adults.
Moreover, other factors such as medications, health conditions, and lifestyle choices can further exacerbate changes in taste perception. For instance, individuals on certain medications may experience a metallic taste or other distortions that can make food less appealing. This can lead to inadequate nutrient intake, potentially affecting overall health.
The Broader Impact on Nutrition and Health
The implications of altered taste perception extend beyond personal enjoyment of food. As individuals find less pleasure in eating, they may unintentionally reduce their calorie intake, leading to unintended weight loss and malnutrition. This trend is especially concerning for older adults who may already be at risk for nutritional deficiencies.
Health professionals emphasize the importance of creating flavorful meals that can stimulate appetite in older adults. Strategies may include enhancing dishes with herbs and spices to compensate for reduced taste sensitivity. By making food more appealing, caregivers and family members can help ensure that older individuals maintain a balanced diet.
In conclusion, the aging process brings significant changes to taste perception, with potential consequences for nutrition and health. Understanding these changes can help in developing strategies to enhance food enjoyment and nutritional intake in older adults. As society continues to age, addressing these challenges will be crucial for promoting well-being and quality of life.