A new report from Sophos highlights significant vulnerabilities in the healthcare sector as the leading cause of ransomware attacks. The State of Ransomware in Healthcare 2025 indicates that exploited vulnerabilities accounted for 33% of incidents, marking a notable shift in the landscape of cyber threats.
The study, which surveyed 292 healthcare providers, underscores the growing resilience of the sector against encryption attacks. However, it also reveals an alarming rise in extortion-only attacks and increasing pressure on IT teams.
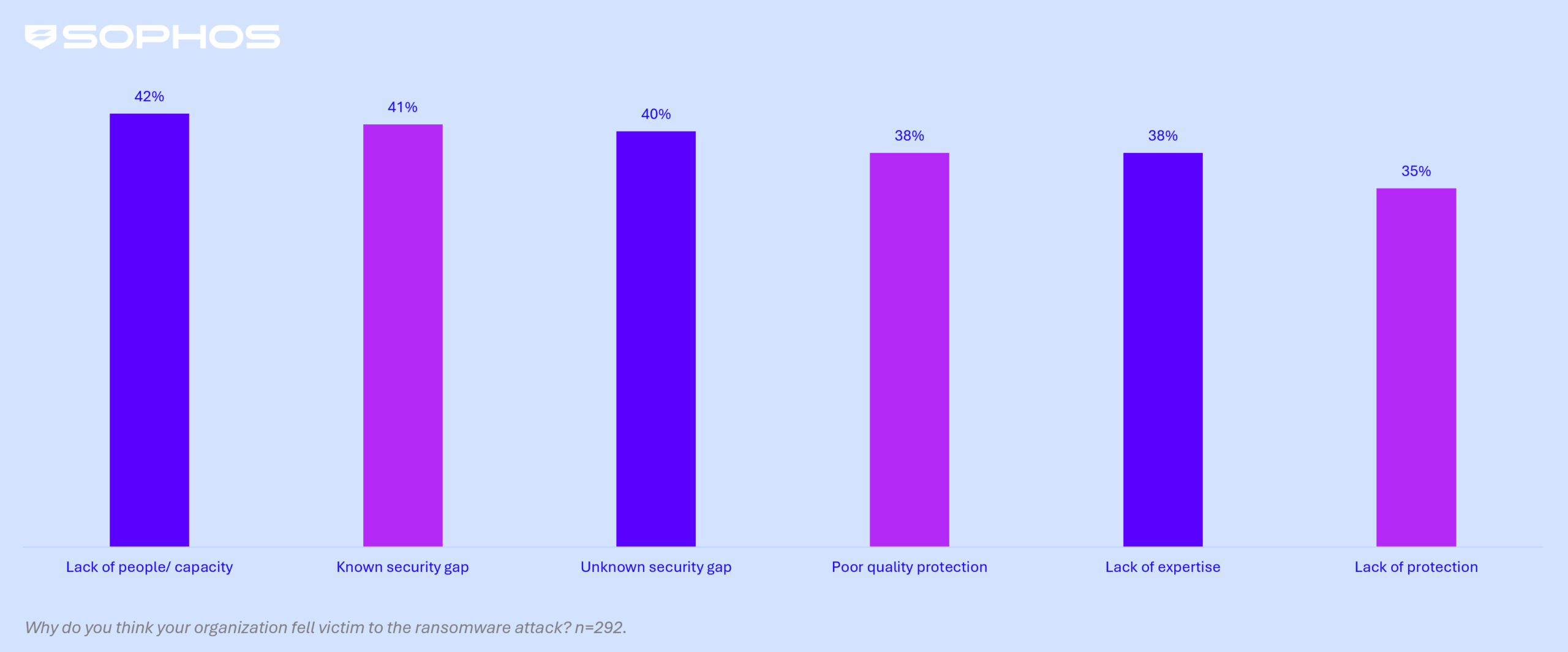
Shifting Causes of Ransomware Attacks
For the first time in three years, exploited vulnerabilities emerged as the most prevalent technical root cause of ransomware incidents. In addition, the report identifies a critical organizational weakness: a lack of personnel dedicated to cybersecurity. 42% of surveyed healthcare providers attributed their vulnerability to insufficient staffing, while 41% cited known security gaps that had not been addressed.
The findings indicate a pressing need for improved staffing and training in cybersecurity roles to bolster defenses against evolving threats.
Trends in Ransomware Economics
The report also highlights a shift in the economics of ransomware within the healthcare sector. As defenses improve against data encryption, cybercriminals have adapted their tactics, leading to an increase in extortion-only attacks. The rate of data encryption in attacks has fallen to its lowest level in five years, with only 34% of attacks resulting in encryption, down significantly from a peak of 74% in 2024.
Conversely, the proportion of healthcare providers facing extortion-only attacks tripled, reaching 12% of all incidents in 2025. This indicates a growing trend where sensitive medical data is stolen without the accompanying encryption that previously characterized many attacks.
Economic pressures on cybercriminals are evident as well. The average ransom demand plummeted by 91% over the past year, dropping from $4 million in 2024 to just $343,000 in 2025. Similarly, the median ransom paid fell from $1.47 million to $150,000, the lowest figure reported across all surveyed sectors.
The cost of recovery has also decreased, with the mean recovery cost (excluding ransom) down by 60% to $1.02 million, compared to $2.57 million in 2024.
Impact on Healthcare Teams
The human toll on healthcare providers is significant, particularly for those affected by data encryption. The report reveals that 39% of IT teams reported increased pressure from senior leaders, and 37% experienced heightened anxiety regarding future attacks.
Despite these challenges, recovery times for healthcare providers have improved. In 2025, 58% of organizations recovered within a week of an incident, nearly tripling the 21% reported in 2024.
Interestingly, the use of backups to restore encrypted data has decreased. Only 51% of healthcare providers utilized backups for recovery, a decline from 72% in 2022. This trend raises concerns about the resilience of backup systems and the confidence healthcare providers have in their recovery strategies.
The findings from Sophos’s report not only shed light on the evolving nature of ransomware in healthcare but also emphasize the urgent need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and staffing to protect sensitive patient data. As the sector continues to navigate these challenges, the call for more robust defenses has never been more critical.