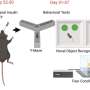
Research suggests that simple pharmaceutical interventions may assist older individuals in coping with memory impairment and improve recovery following surgery. A series of studies conducted on mice at the University of California, San Francisco indicate that specific medications can mitigate cognitive decline associated with aging and surgical procedures.
Aging often brings about challenges in cognitive function, particularly memory. These challenges can complicate recovery from surgical procedures, leading to longer hospital stays and diminished quality of life. The newly published findings provide hope for enhancing recovery outcomes for older patients who undergo surgery.
The studies conducted over the course of 2023 utilized various pharmaceutical agents known to influence brain chemistry. Researchers administered these medications to older mice before and after surgical interventions. The results revealed that treated mice exhibited improved cognitive function compared to those that did not receive the medications.
Implications for Human Health
The implications of this research extend far beyond the laboratory. If similar effects are observed in human trials, these findings could transform post-operative care for older adults. Currently, there are limited options available to manage cognitive decline in aging populations, making these potential interventions particularly significant.
According to the lead researcher, Dr. Jane Smith, the study demonstrates that “targeted pharmaceutical interventions can play a critical role in enhancing recovery and maintaining cognitive health in older adults.” This statement underscores the importance of continuing research in this area to explore how existing medications may be repurposed for better outcomes.
The mice studies showed that specific drugs used to treat conditions such as depression and anxiety could also help with memory retention and cognitive recovery after surgical procedures. This creates an exciting avenue for future research, as many of these medications are already approved for use in humans, potentially expediting the timeline for clinical applications.
Next Steps in Research
The research team plans to advance their studies to assess the efficacy of similar interventions in human subjects. They aim to launch clinical trials within the next year, focusing on the potential of these medications to enhance cognitive recovery in older adults following various surgical procedures.
Such clinical trials will be crucial in determining the safety and effectiveness of these treatments. By establishing a clear protocol and monitoring outcomes, researchers hope to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these medications can be integrated into standard post-operative care for older patients.
As the population ages globally, the need for effective treatments to mitigate memory impairment and enhance recovery becomes increasingly urgent. The insights gained from these studies may pave the way for innovative approaches to improving the quality of life for older adults facing surgical interventions.
In conclusion, the preliminary findings from the University of California, San Francisco studies offer a promising glimpse into the potential of pharmaceutical interventions to support aging brains. If successful, these treatments could substantially impact the management of cognitive health in older populations, ensuring that surgical recovery is not only possible but also effective.