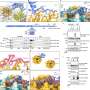
Research from the University of California, San Francisco, has revealed that when ribosomes, the essential protein-producing machines within cells, collide, the cells initiate emergency stress defenses. This discovery sheds light on how cells manage critical disruptions during protein synthesis, a vital process for all living organisms.
Ribosomes play a key role in translating the genetic code carried by messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins by linking amino acids in specific sequences. This function is crucial for maintaining cellular health and function. When ribosomes operate smoothly, they contribute to the seamless production of proteins necessary for various cellular processes.
However, complications can arise when ribosomes encounter obstacles while moving along the mRNA. The research indicates that collisions between ribosomes can lead to serious inefficiencies in protein production. These collisions may occur due to various factors, including high levels of stress or abnormal changes in the cellular environment.
Emergency Responses Triggered by Ribosome Collisions
The study highlights a sophisticated response system activated by cells when ribosomes collide. In response to these stressful encounters, cells activate protective mechanisms designed to mitigate damage. This includes the upregulation of stress response genes that help restore normal protein synthesis levels and overall cellular function.
The findings underscore the importance of ribosome integrity and the consequences of their malfunction. The collision of ribosomes not only disrupts protein synthesis but also poses a risk to cellular health by potentially leading to the accumulation of faulty proteins. This can have detrimental effects, especially in rapidly dividing cells or during periods of increased cellular demand.
Researchers utilized advanced imaging techniques to observe ribosome behavior in real time. By tracking the interactions of ribosomes with mRNA, they were able to capture moments of collision and assess the subsequent cellular responses. This innovative approach provided valuable insights into the dynamic processes occurring within cells.
Implications for Understanding Cellular Stress
Understanding how cells respond to ribosome collisions has broader implications for health and disease. Disruptions in protein synthesis are linked to various disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. By studying these emergency stress responses, researchers hope to identify potential therapeutic targets for treating such conditions.
The research team emphasizes the need for further investigation into the mechanisms underlying ribosome collisions and the cellular stress responses that follow. As scientists continue to uncover the complexities of cellular function, this study serves as a critical step toward improving our understanding of cellular resilience and the maintenance of health.
The findings were published in a recent issue of *Nature Communications* and represent a significant advancement in cellular biology. As the scientific community delves deeper into these processes, the implications for biomedical research and therapeutic development are profound.
Overall, this research highlights the remarkable adaptability of cells in the face of disruption and the intricate dance of ribosomes as they navigate the challenges of protein synthesis. As we learn more about these functions, we may uncover new strategies for promoting cellular health and combating diseases linked to protein synthesis errors.