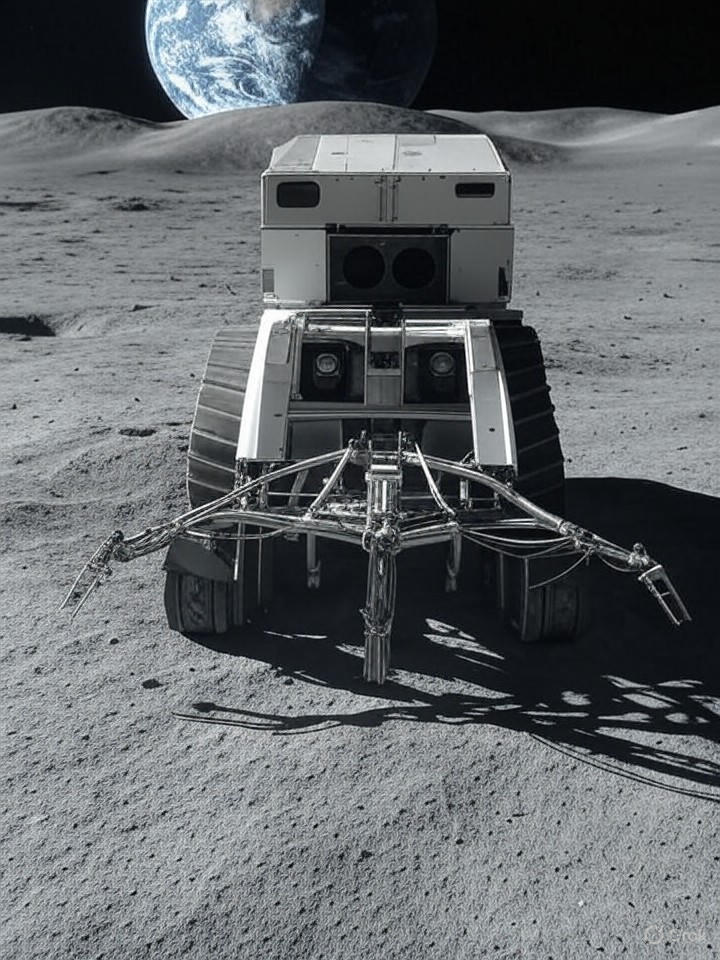
A pioneering mining company, Interlune, has announced significant progress in its plans to extract helium-3 from the lunar surface by March 2028. This rare isotope, which holds potential for revolutionizing energy production and various high-tech applications, is drawing increasing interest as nations and private entities look to tap into the moon’s resources. Interlune claims it has identified substantial helium-3 deposits, marking a potential milestone in the field of space mining.
The company’s announcement highlights the growing commercial viability of lunar resource extraction. Helium-3, produced by billions of years of solar wind exposure on the moon, offers a non-radioactive alternative to traditional energy sources. With estimates placing its market value at up to $20 million per kilogram, helium-3 is seen as a vital component for future nuclear fusion reactors. These reactors promise to provide clean, virtually limitless energy, addressing global energy demands.
Geopolitical Implications of Lunar Resource Extraction
The push for helium-3 mining comes amid rising competition between global superpowers. The United States and China are leading efforts to establish lunar dominance, as reported by Space.com. Interlune’s plans align with broader ambitions to secure helium-3 for applications in quantum computing, where it is utilized as a critical coolant for advanced systems. The company has already entered agreements to supply up to 10,000 liters of extracted helium-3, signaling early confidence in market demand.
To facilitate extraction, Interlune has developed a prototype harvester capable of processing 110 tons of lunar soil per hour. This advancement, noted in coverage by The Washington Post, addresses the logistical challenges of operating on the moon, including extreme temperatures and the lack of atmosphere. The design aims to minimize environmental disruption while maximizing efficiency in resource extraction.
Technological Innovations and Economic Considerations
The applications of helium-3 extend beyond energy production. It plays a crucial role in medical imaging and supercomputing, where its scarcity on Earth has driven prices significantly higher. As detailed by Forbes, Interlune is working on autonomous robotic systems for mining operations, with plans for deployment in tandem with NASA’s Artemis program and China’s Chang’e missions. These initiatives could provide the necessary infrastructure for transporting and processing lunar resources.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain. The high costs of space travel and the uncertain economics of returning materials to Earth pose significant hurdles. Proponents of lunar mining argue that in-situ resource utilization—using materials found on the moon—could mitigate costs and support sustainable operations. As highlighted in Interesting Engineering, global superpowers view helium-3 as a strategic asset, with nations like Russia also entering the competition, potentially reshaping the landscape of energy geopolitics.
Investment in this venture is growing, with Interlune attracting funding to deploy advanced multispectral cameras for precise resource mapping. A partnership with quantum cryogenics firm Bluefors, reported by Gizmodo, marks one of the largest contracts related to space resources to date, underscoring the advancing role of helium-3 in enhancing computational capabilities.
Ethically, the race for lunar resources raises questions about equitable access under the Outer Space Treaty. Critics caution against a potential new colonialism, while supporters argue for the shared technological benefits that could arise from advancements in fusion energy, which could help combat climate change.
Looking ahead, successful helium-3 mining operations could catalyze a broader space economy, encompassing the extraction of water ice, rare earth elements, and oxygen from lunar soil. Insights from 21st Century Tech Blog suggest that these developments could support permanent lunar settlements, reducing reliance on Earth-supplied resources.
For stakeholders in this emerging industry, the focus will be on scalability. If Interlune’s prototypes prove successful, the influx of investment could transform space from a scientific frontier into a lucrative commercial domain. This lunar initiative represents a pivotal shift, positioning the moon as a battleground for technological innovation and economic growth. As extraction technologies advance, the vision of harnessing cosmic resources edges closer to reality, promising significant impacts on Earth’s future energy landscape.