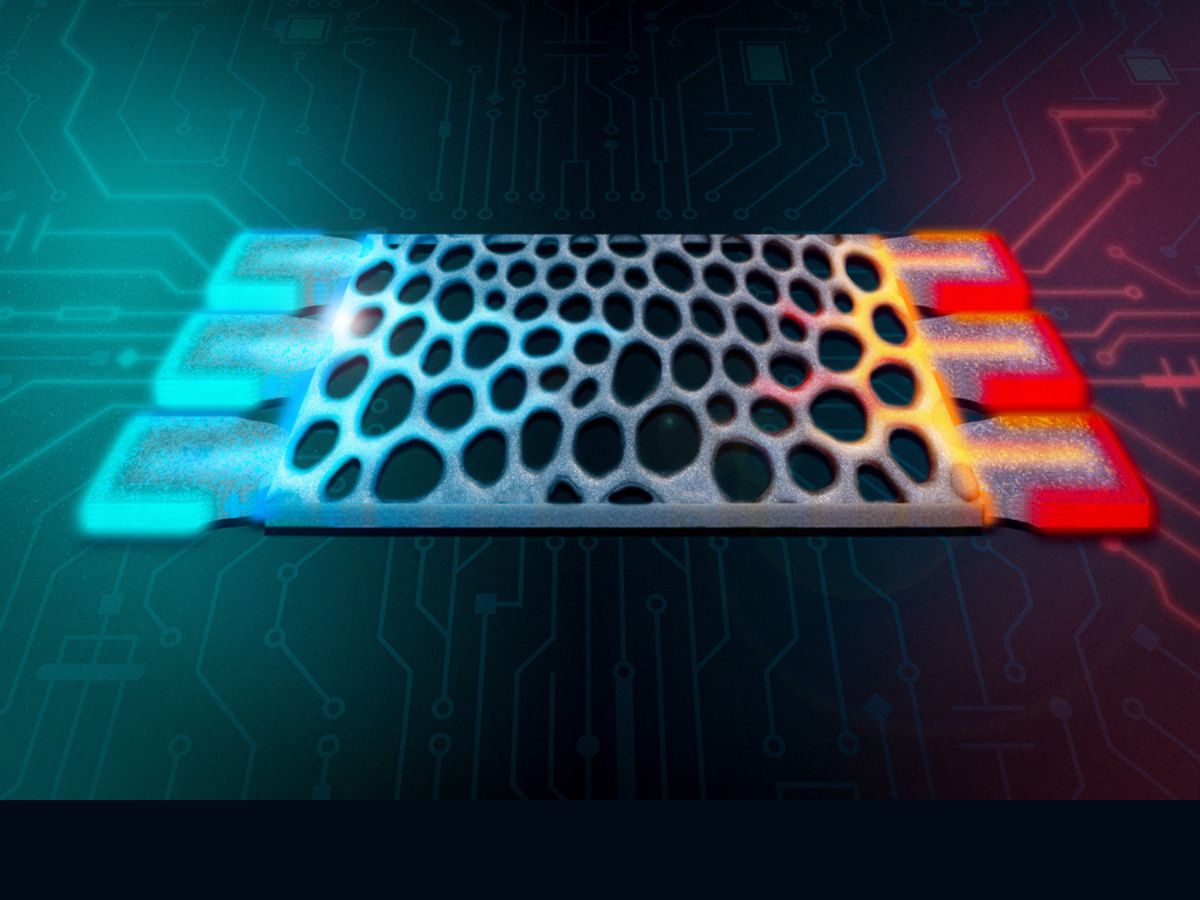
Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed innovative silicon structures that convert waste heat into usable computing power. This breakthrough could significantly enhance energy efficiency in computing, addressing a growing need for sustainable energy solutions in technology.
The research, detailed in a recent publication in APS Journals, outlines how excess heat generated by electronic devices can be harnessed rather than discarded. By utilizing these silicon structures, MIT engineers created a method to transform waste heat into electrical energy, which can subsequently be used to power computing devices.
Innovative Approach to Energy Efficiency
Current computing technology often struggles with efficiency, as a considerable amount of energy is lost as heat during processing. The MIT team’s approach focuses on silicon’s unique properties to capture and convert this heat into power effectively. This method not only reduces energy waste but also lowers the environmental impact associated with traditional energy consumption.
The researchers emphasized that their technology could play a crucial role in the quest for more sustainable energy solutions. By integrating this waste heat recovery system into existing electronic devices, manufacturers could enhance the overall energy efficiency of computers and other electronics.
The potential applications of this technology are vast, ranging from personal computers to large data centers, which consume substantial energy. The ability to recycle waste heat could lead to significant cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint for businesses and consumers alike.
Implications for Future Technology
As digital transformation accelerates worldwide, the demand for efficient computing power continues to grow. According to the team at MIT, this technology could help bridge the gap between energy consumption and sustainable practices in the tech industry. By capturing waste heat, the silicon structures could contribute to a more circular economy, where energy resources are utilized more effectively.
The MIT engineers have indicated that further research and development will be necessary to optimize the efficiency of these silicon structures. However, the initial results are promising, suggesting a viable pathway for future innovations in energy-efficient computing.
This advancement is a significant step towards minimizing energy waste in technology. By converting waste heat into a resource, MIT’s engineers are not only addressing immediate energy challenges but also paving the way for a more sustainable future in electronics.